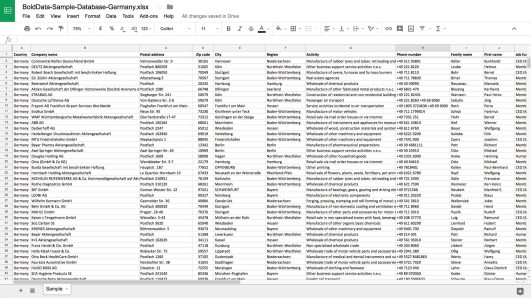
The parent company, or holding company, owns a controlling interest in one or more subsidiaries. The parent company holds a significant share in the subsidiary, allowing it to exert considerable influence over its operations, policies, and decision-making.
What is the Purpose of a Parent Company?
The primary purpose of a parent company is to own and manage the subsidiaries it has invested in. The parent company is responsible for providing the subsidiary with financial and operational support and making strategic decisions that will benefit both the parent company and the subsidiary.
What is the Relationship between a Parent Company and its Subsidiaries?
The relationship between a parent company and its subsidiaries involves control and ownership. The parent company holds a controlling interest in the subsidiary, meaning it can make decisions that impact its operations, policies, and overall success. At the same time, the subsidiary operates as its entity, with its management and employees.
How Does a Parent Company Benefit from its Subsidiaries?
A parent company benefits from its subsidiaries in several ways. For example, the parent company can spread its risk across multiple businesses, allowing it to mitigate the impact of any potential losses in one business. Additionally, the parent company may leverage each subsidiary’s strengths to achieve its overall business goals and objectives.
What are the Different Types of Parent Companies?
There are two main parent company types: pure holding and mixed holding companies. Pure holding companies own and manage a portfolio of subsidiaries but do not have any active business operations. While mixed holding companies, on the other hand, both own and manage subsidiaries and have their business operations.
Key Takeaways
To sum it up, a parent company is a company that owns and manages one or more subsidiaries. The purpose of a parent company is to provide financial and operational support to its subsidiaries and make strategic decisions that will benefit both the parent company and the subsidiary.
The relationship between a parent company and its subsidiary involves control and ownership. A Parent company benefits from its subsidiaries in several ways, such as spreading risk and leveraging the strengths of each subsidiary. Last but not least, there are two main parent company types: pure holding and mixed holding companies.
Looking for A Trusted Source of Company Data?
BoldData will help you reach thousands of potential clients based on demographics related to your product or service. Get a list of companies in any country narrowed down by our data experts. Contact us today to learn more!